What is a Tooth Abscess?
A tooth abscess is a dental condition that occurs when there is a bacterial infection in the tooth. It is a result of untreated dental decay or trauma to the tooth. The infection can spread to the root and surrounding tissues, forming a pocket of pus known as an abscess.
There are two main types of tooth abscess: periapical abscess and periodontal abscess. A periapical abscess occurs when bacteria invade the dental pulp, which is the innermost part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. On the other hand, a periodontal abscess happens when there is an infection in the gum tissue or periodontal pocket.
The primary cause of a tooth abscess is poor dental hygiene. When plaque and food particles are not properly removed from the teeth, they can lead to dental decay and gum disease. These conditions create an environment for bacteria to thrive and cause an infection. Other risk factors for developing a tooth abscess include a weakened immune system, cracked or chipped teeth, and previous dental procedures.
Signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess
The signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess can vary depending on the severity and location of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Severe toothache
- Swelling in the face or cheek
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Fever
- Tender or swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty chewing or biting
- Bad breath or unpleasant taste in the mouth
Home Remedies for Managing Tooth Abscess

Topical pain relief and natural remedies
There are some home remedies that can provide temporary relief from the pain and discomfort caused by a tooth abscess. These remedies are not a substitute for professional dental care, but they can help manage the symptoms and promote healing.
One popular natural remedy is rinsing the mouth with warm saltwater. This can help reduce inflammation and draw out the pus from the abscess. To make a saltwater rinse, dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in eight ounces of warm water and swish it around in your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out. Repeat this several times a day.
Another natural remedy is applying a cold compress to the affected area. This can help numb the pain and reduce swelling. Wrap a few ice cubes in a thin cloth and hold it against your cheek or jaw for 15 minutes at a time. Be sure to take breaks in between to prevent skin damage.
Home-care practices to reduce discomfort and swelling
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial. Brush your teeth gently twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove any food particles and bacteria from between your teeth.
Using a warm compress can also help alleviate pain and swelling. Soak a clean cloth in warm water and wring out the excess. Hold the warm compress against your cheek or jaw for about 15 minutes at a time, repeating as needed. This can help promote blood circulation and reduce inflammation.
Avoiding foods and drinks that are hot, cold, or high in sugar can also help minimize sensitivity and discomfort. Stick to soft foods that are easy to chew and swallow.
It is important to note that these home remedies and practices are not a substitute for professional dental care. If you have a tooth abscess, it is crucial to seek prompt treatment from a dentist to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications.
Antibiotics for Tooth Abscess
Types of antibiotics commonly prescribed
When it comes to treating a tooth abscess, antibiotics are often prescribed by dentists to help combat the bacterial infection. These medications work by killing the bacteria causing the infection and reducing inflammation.
Amoxicillin is often the first-line antibiotic used for tooth abscess. It is effective against a wide range of bacteria and has a low risk of side effects. Clindamycin is another commonly used antibiotic, especially for those who are allergic to penicillin. Metronidazole is often prescribed in combination with other antibiotics to target specific bacterial strains. Cephalexin and azithromycin are also effective options in certain cases.
Potential side effects and precautions
While antibiotics can be effective in treating tooth abscess, they can also have potential side effects and considerations to keep in mind:
- Common side effects may include diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, it is important to contact your healthcare provider.
- Some antibiotics can interact with other medications, so it is important to inform your dentist or doctor about any other medications you are taking.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals may have specific considerations, and it is important to discuss the use of antibiotics with a healthcare professional.
- It is crucial to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your dentist or doctor, even if symptoms improve. This helps ensure that the infection is fully treated and prevents the development of antibiotic resistance.
Remember, antibiotics should only be used under the guidance and prescription of a healthcare professional. They are not a substitute for dental care and should be complemented with appropriate dental treatment to fully resolve the tooth abscess.
Drainage and Root Canal Therapy
To effectively treat a tooth abscess, it is crucial to address the source of the infection and promote drainage of the pus-filled pocket. Draining the abscess helps relieve pain, reduce swelling, and prevent the spread of infection. In some cases, the dentist may need to create an incision to allow the pus to escape.
Drainage is typically done by:
- Making a small hole in the abscess to release the pus
- Using a needle or a drainage tube to drain the fluid
- Irrigating the area to remove any remaining debris
The dentist may also prescribe antibiotics to further control the infection and promote healing. However, drainage is essential to remove the accumulated pus and ensure a successful recovery.
Understanding root canal therapy and its effectiveness
In cases where the tooth abscess is caused by an infection inside the tooth, root canal therapy may be recommended. Root canal therapy involves removing the infected pulp and nerves from the tooth’s root canal system.
During the procedure, the dentist will:
- Numb the area around the tooth with a local anesthetic.
- Create an access hole to reach the infected pulp chamber.
- Remove the diseased pulp, clean the canals, and shape them for filling.
- Fill the canals with a rubber-like material called gutta-percha.
- Seal the access hole with a temporary or permanent filling.
Root canal therapy allows the tooth to be saved and prevents the spread of infection to other teeth or the jawbone. The procedure is highly effective in treating tooth abscess and eliminating associated pain.
Tooth Extraction as a Treatment Option
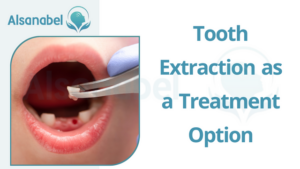
When tooth extraction is necessary
In some cases, tooth extraction may be necessary to treat a tooth abscess. This is typically considered when other treatment options, such as drainage and root canal therapy, have failed or are not possible. Tooth extraction is done to remove the infected tooth and prevent the spread of infection to surrounding teeth and tissues.
Tooth extraction may also be required if the tooth has severe damage or decay that cannot be effectively treated or repaired. In these situations, removing the tooth may be the best course of action to prevent further complications and restore oral health.
Care after tooth extraction
After a tooth extraction, it is important to follow proper care instructions to promote healing and prevent complications. These instructions may include:
- Gently biting down on a gauze pad to control bleeding
- Using ice packs to reduce swelling
- Taking prescribed pain medication or over-the-counter pain relievers
- Eating soft foods and avoiding chewing on the extraction site
- Maintaining good oral hygiene, except for the extraction site
Tooth replacement options
After a tooth extraction, it may be necessary to replace the missing tooth to restore proper chewing function and prevent shifting of the surrounding teeth. Some tooth replacement options include:
- Dental Implants: Implants are titanium posts surgically placed into the jawbone to support a dental crown. They offer a permanent and natural-looking solution.
- Dental Bridges: A bridge consists of artificial teeth attached to crowns on neighboring teeth. It bridges the gap left by the extracted tooth.
- Dentures: Removable dentures can be used to replace multiple missing teeth. They can be partial or complete dentures.Your dentist will evaluate your specific case and recommend the most suitable tooth replacement option for you.
Local anesthesia and sedation options during dental procedures
To manage pain during dental procedures, local anesthesia is commonly used. This numbs the area around the tooth, preventing any pain or discomfort during the treatment. Your dentist may also offer sedation options to help you relax during the procedure, such as nitrous oxide (laughing gas) or oral sedatives. These options can help alleviate anxiety and make the experience more comfortable for patients.
Pain medication and techniques to manage pain at home
After a tooth extraction or dental procedure, it is common to experience some pain or discomfort. Your dentist may prescribe pain medication to help manage this. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions provided by your dentist. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also be taken to alleviate pain.
In addition to medication, there are some techniques you can use to manage pain at home:
- Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce swelling and numb the area, providing pain relief.
- Eating soft foods and avoiding chewing on the extraction site can prevent added discomfort.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene, except for the extraction site, can help promote healing and prevent infection.
It is crucial to follow your dentist’s post-operative instructions and consult them if you have any concerns or if the pain persists or worsens. They can provide further guidance on pain management techniques or adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
How to Prevent Tooth Abscess
Oral hygiene practices to prevent tooth abscess
Tooth abscesses can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Here are some tips to help prevent tooth abscess:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. This helps remove bacteria and plaque from the surface of your teeth.
- Floss daily to clean between your teeth and remove any food particles that may be trapped.
- Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can contribute to tooth decay and increase the risk of abscess formation.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Regular dental check-ups and their role in preventing abscesses
Regular dental check-ups play a vital role in preventing tooth abscesses. During these visits, your dentist can identify early signs of tooth decay or gum disease, which can lead to abscess formation. Your dentist will:
- Perform a thorough examination to check for any dental issues that could contribute to abscess formation.
- Take X-rays to detect any hidden cavities or infections.
- Clean your teeth to remove plaque and calculus buildup, reducing the risk of infection.
- Provide professional advice on oral hygiene and lifestyle habits that can help prevent tooth abscesses.
By visiting your dentist regularly, they can monitor your oral health and address any concerns before they develop into more serious issues, such as tooth abscesses. Prevention is key, and taking proactive steps to maintain good oral hygiene and attend regular dental check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of tooth abscesses.
Complications and Risks Associated with Tooth Abscess
Possible complications if left untreated
If a tooth abscess is left untreated, it can lead to several complications, including:
- Spread of infection: The infection from the abscess can spread to the surrounding tissues, including the gums, jawbone, and even the sinuses. This can result in a more severe infection, which may require more aggressive treatment.
- Cellulitis: Untreated tooth abscess can cause cellulitis, a bacterial infection of the soft tissues. Cellulitis can be painful, and if not treated promptly, it can spread to other parts of the face and head.
- Ludwig’s angina: This is a rare but serious complication of a tooth abscess. It occurs when the infection spreads to the floor of the mouth and neck, leading to swelling and difficulty in breathing.
- Sepsis: In severe cases, the infection from a tooth abscess can enter the bloodstream, leading to a condition called sepsis. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Potential risks and long-term consequences
Apart from the immediate complications, tooth abscess can also have long-term consequences and risks, including:
- Tooth loss: If the infection is not treated promptly, it can lead to the destruction of the tooth structure and its supporting tissues. This can result in the need for tooth extraction.
- Recurrence of abscess: If the underlying cause of the abscess, such as tooth decay or gum disease, is not addressed, there is a risk of the abscess recurring in the future.
- Damage to adjacent teeth: The infection from the abscess can spread to the neighboring teeth, causing damage to their structures and increasing the risk of further complications.
- Facial deformity: In severe cases where the infection causes extensive destruction of the jawbone, it can lead to facial deformity and loss of facial symmetry.
To prevent these complications and risks, it is essential to seek prompt dental treatment if you suspect a tooth abscess. Early intervention can help prevent the spread of infection and preserve the affected tooth. Regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene habits will also contribute to reducing the risk of tooth abscess and its associated complications.
Summary of different treatment options for tooth abscess
In summary, there are several treatment options available for tooth abscess. The most common approaches include:
- Root canal treatment: This procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth and cleaning the root canal before filling it with a biocompatible material.
- Dental extraction: In cases where the tooth is severely damaged or the infection cannot be effectively treated with a root canal, the tooth may need to be extracted.
- Incision and drainage: For larger abscesses, a minor surgical procedure may be needed to drain the pus and relieve pressure on the affected area.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the infection and prevent its spread. However, antibiotics alone are not sufficient to treat a tooth abscess and should be used in conjunction with other dental treatments.
Choosing the right treatment approach and seeking professional dental care
It is important to note that seeking professional dental care is crucial when dealing with a tooth abscess. A qualified dentist will be able to assess the severity of the abscess and recommend the most appropriate treatment approach.
When choosing a treatment option, factors such as the extent of the infection, the condition of the affected tooth, and the patient’s overall oral health should be taken into consideration. The dentist will also consider the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option before making a recommendation.
In any case, it is not recommended to attempt self-treatment or ignore a tooth abscess. Prompt dental care can prevent complications and long-term consequences associated with tooth abscess, such as the spread of infection, tooth loss, damage to adjacent teeth, and facial deformity.
Taking care of your oral health through regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day and flossing, can prevent tooth decay and gum disease, which are common underlying causes of tooth abscess.
Remember, early intervention and professional dental care are key to successfully treating a tooth abscess and maintaining your overall oral health.
