Definition and symptoms of tooth abscess
A tooth abscess is a dental condition characterized by an infection at the root of a tooth or in the space between the gums and teeth. It occurs when bacteria enter the tooth through a dental cavity, chip, or crack, leading to the formation of pus.
Common symptoms of tooth abscess include severe and persistent toothache, swelling of the face or jaw, redness and tenderness in the gums, bad breath, and a bitter taste in the mouth. In some cases, the abscess may rupture, resulting in a foul-tasting and foul-smelling discharge.
Causes and risk factors of tooth abscess
Tooth abscesses are primarily caused by bacterial infections. The most common bacteria involved are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus strains. These bacteria enter the tooth through dental cavities or cracks in the enamel, spreading to the root and surrounding tissues.
Poor oral hygiene, including inadequate brushing and flossing, can increase the risk of developing a tooth abscess. Other risk factors include frequent consumption of sugary and acidic foods, smoking, a weakened immune system, and certain systemic conditions like diabetes.
It is important to seek dental treatment if you suspect a tooth abscess as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Treatment usually involves draining the abscess and removing the source of infection through a root canal or tooth extraction.
Antibiotics may also be prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent its spread. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, along with routine dental check-ups, can help prevent tooth abscesses.
Types of Tooth Abscess
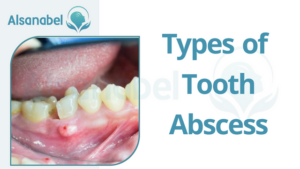
Periapical abscess
A periapical abscess is the most common type of tooth abscess, usually occurring as a result of an untreated dental cavity. The bacteria invade the innermost part of the tooth, known as the pulp, causing an infection and leading to the formation of pus. As the infection progresses, it can spread to the surrounding tissues, causing pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
Other symptoms may include tooth sensitivity, foul taste in the mouth, and the formation of a pimple-like bump on the gums near the infected tooth.
Periodontal abscess
A periodontal abscess, also known as a gum abscess, occurs when bacteria infect the gums and the supportive structures around the tooth. This type of abscess is often caused by gum disease or a foreign object trapped between the tooth and the gum. The bacteria multiply and produce toxins, leading to inflammation, swelling, and the formation of pus pockets in the gums.
Symptoms of a periodontal abscess include severe gum swelling, throbbing pain, a bad taste in the mouth, loose teeth, and difficulty in biting or chewing.
It is vital to seek prompt dental treatment for any type of tooth abscess to prevent further complications. Depending on the severity and location of the abscess, treatment may involve draining the pus, cleaning the affected area, and removing the source of infection through a root canal or tooth extraction.
Antibiotics may also be prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce the risk of spreading. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, is essential in preventing tooth abscesses and maintaining overall oral health.
Potential Complications of Tooth Abscess
Spread of infection to nearby areas
If left untreated, a tooth abscess can spread the infection to nearby areas, leading to more serious complications. The infection can spread to the jawbone, causing osteomyelitis, which is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition. The infection can also spread to the sinuses, leading to sinusitis, or to the bloodstream, causing a condition known as sepsis. These complications can cause significant pain, swelling, and can even affect overall health.
Development of a dental cyst
In some cases, a tooth abscess can lead to the development of a dental cyst. A dental cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the jawbone or surrounding tissues. Cysts can cause swelling, pain, and can even lead to damage to the surrounding teeth and bone. Treatment for a dental cyst typically involves surgical removal and addressing the underlying cause.
Formation of a dental fistula or sinus tract
A dental abscess can also lead to the formation of a dental fistula or sinus tract. This occurs when the infection creates a channel from the abscess to the surface of the gums or skin. A fistula or sinus tract can cause a constant drainage of pus, a foul taste in the mouth, and may be accompanied by swelling and pain. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying infection and sometimes surgical intervention to close the fistula or tract.
Abscess Treatment Options
Root canal therapy: procedure and benefits
Root canal therapy is a common treatment option for tooth abscesses. It involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth and cleaning the roots to eliminate the infection. Here is an overview of the procedure and its benefits:
- Procedure: The dentist will start by numbing the area around the affected tooth with local anesthesia. They will then create a small opening in the tooth to access the infected pulp. The infected pulp is carefully removed, and the canals are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected. Once the canals are clean, they are filled with a special material called gutta-percha, and the tooth is sealed with a temporary filling or crown.
- Benefits: Root canal therapy has several benefits, including:
- Preservation of the natural tooth: By removing the infected pulp and saving the tooth, root canal therapy avoids the need for extraction and the potential for further complications.
- Relief from pain: Root canal therapy can alleviate the severe pain caused by a tooth abscess.
- Restoration of functionality: After the procedure, the tooth can function normally, allowing you to bite and chew without discomfort or limitations.
Tooth extraction: when it’s necessary and what to expect
In some cases, a tooth extraction may be necessary to treat a tooth abscess. Here’s what you can expect from the procedure:
- Procedure: The dentist will administer local anesthesia to numb the area around the affected tooth. They will then carefully loosen and remove the tooth from its socket. After extraction, the dentist may prescribe pain medication or recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to manage any post-operative discomfort.
- Reasons for extraction: Tooth extraction may be necessary if:
- The tooth is severely damaged or decayed and cannot be saved through other treatments.
- The infection has spread to the surrounding tissues or bone.
- The tooth is causing severe pain or affecting overall oral health.
- Post-extraction care: After extraction, it is important to follow your dentist’s instructions for care to promote proper healing. This may include taking antibiotics, avoiding certain foods or activities, and practicing good oral hygiene.
Pain Management and Self-Care

Over-the-counter pain relievers for tooth abscess
When experiencing pain from a tooth abscess, over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief. Commonly used medications include:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): This nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with a tooth abscess. Follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications.
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): This pain reliever can also help alleviate tooth abscess pain. However, it is important to note that acetaminophen does not have anti-inflammatory properties. Again, follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional as needed.
Taking an over-the-counter pain reliever can provide temporary relief, but it is crucial to seek professional dental care to address the underlying cause of the tooth abscess.
Home remedies and self-care tips for pain relief
While professional dental treatment is necessary for addressing a tooth abscess, there are some self-care tips and home remedies that can provide temporary pain relief. These include:
- Warm saltwater rinses: Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in eight ounces of warm water and swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out. Saltwater rinses can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Cold compress: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area can help numb the pain temporarily and reduce swelling.
- Soft foods and proper oral hygiene: Stick to soft foods that are easy to chew to minimize discomfort. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and flossing can help prevent further infection.
It is important to note that while these home remedies and self-care tips can provide temporary relief, they do not substitute professional dental treatment. Consulting with a dentist is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment of a tooth abscess.
Preventing Tooth Abscess
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices
To prevent tooth abscesses, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, using a fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily. Proper brushing and flossing can help remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums, reducing the risk of infection. Additionally, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can further help eliminate bacteria and maintain oral health.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for preventing tooth abscesses. Dentists can identify early signs of dental problems, such as cavities or gum disease, and provide appropriate treatment before they progress to an abscess. During a dental cleaning, the dentist can remove plaque and tartar buildup that can contribute to infections. It is recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year or as recommended by your dental professional.
individuals can reduce the risk of developing a tooth abscess. Furthermore, if any signs or symptoms of a tooth abscess, such as persistent tooth pain, swelling, or a bad taste in the mouth, occur, it is important to seek immediate dental care. Prompt treatment can prevent the spread of infection and alleviate pain and discomfort.
Dental Abscess and Systemic Health
Untreated tooth abscesses can have a significant impact on systemic health. The infection from a tooth abscess can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, increasing the risk of various health complications. Several studies have found a link between dental abscesses and systemic conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: The bacteria from an abscessed tooth can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the development of heart disease. It can cause inflammation in the blood vessels, increase the risk of blood clots, and potentially lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to infections, including tooth abscesses. Conversely, an untreated abscess can make it harder to control blood sugar levels, leading to complications in managing diabetes.
- Respiratory Infections: The bacteria from an abscessed tooth can also spread to the respiratory system, causing infections such as pneumonia or bronchitis. This is particularly concerning for individuals with weakened immune systems.
Effects of untreated dental abscess on overall health
Neglecting treatment for a dental abscess can have detrimental effects on overall health. Some of the potential consequences include:
- Chronic Pain and Discomfort: An untreated dental abscess can cause severe toothaches, facial swelling, and persistent discomfort. This can hinder eating, speaking, and overall quality of life.
- Facial Cellulitis: If the infection spreads beyond the tooth and into the surrounding tissues, it can lead to a condition called facial cellulitis. This causes inflammation, redness, and warmth in the facial area, and may require hospitalization for treatment.
- Septicemia: In severe cases, the infection can lead to septicemia, a life-threatening condition where bacteria enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This can result in organ failure, shock, and even death if not promptly treated.
It is crucial to address dental abscesses promptly to prevent these potential health complications. Seeking immediate dental care at the first signs of a tooth abscess, such as severe tooth pain or swelling, is essential. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene practices can further reduce the risk of dental abscesses, promoting overall systemic health and well-being.
Dental Abscess in Children
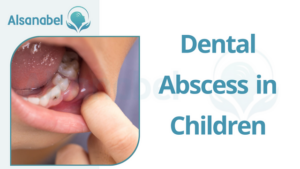
Special considerations for tooth abscess in children
Children can also experience dental abscesses, although there are some special considerations to keep in mind when it comes to their oral health. Here are a few key points:
- Tooth Decay: Tooth decay is a common underlying cause of dental abscesses in children. It is important for parents to emphasize good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, to prevent tooth decay and, subsequently, dental abscesses.
- Primary Teeth: Dental abscesses can occur in both primary (baby) teeth and permanent teeth. Even though primary teeth will eventually be replaced by permanent teeth, treating dental abscesses in primary teeth is vital to prevent the spread of infection and maintain oral health.
- Pain and Discomfort: Children may have a difficult time expressing their dental pain or discomfort. Parents should watch for signs such as persistent crying, irritability, difficulty eating, or avoiding certain foods. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek dental care as soon as possible.
Treatment options and prevention strategies
Treating dental abscesses in children typically involves a combination of oral antibiotics and dental procedures. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the abscess and the child’s overall oral health. Dental procedures may include draining the abscess, root canal treatment, or extraction of the affected tooth.
Preventing dental abscesses in children can be achieved through the following strategies:
- Regular dental check-ups: Bringing children to the dentist at regular intervals allows for early detection of tooth decay or other oral health issues, reducing the risk of dental abscesses.
- Good oral hygiene: Teaching children proper brushing and flossing techniques and ensuring they practice them consistently can minimize the chance of tooth decay and subsequent abscesses.
- Healthy diet: Limiting sugary snacks and drinks can help prevent dental decay and reduce the risk of abscesses.
- Fluoride use: Using fluoride toothpaste and receiving professional fluoride treatments can strengthen tooth enamel and decrease the likelihood of tooth decay.
Importance of early detection and prompt treatment
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial when it comes to dental abscesses in children. Tooth decay is a common underlying cause of dental abscesses in children, so parents should emphasize good oral hygiene practices to prevent tooth decay and subsequent abscesses. Regular brushing and flossing should be encouraged.
Dental abscesses can occur in both primary (baby) teeth and permanent teeth. Although primary teeth will eventually be replaced by permanent teeth, it is important to treat dental abscesses in primary teeth to prevent the spread of infection and maintain oral health.
It’s important for parents to be vigilant for signs of dental pain or discomfort in their children. Children may have a difficult time expressing their pain, so parents should watch for signs such as persistent crying, irritability, difficulty eating, or avoiding certain foods. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek dental care as soon as possible.
Summary of potential complications and prevention tips
Treating dental abscesses in children typically involves a combination of oral antibiotics and dental procedures. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the abscess and the child’s overall oral health. Dental procedures may include draining the abscess, root canal treatment, or extraction of the affected tooth.
Preventing dental abscesses in children can be achieved through regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, maintaining a healthy diet, and using fluoride. Regular dental check-ups allow for early detection of tooth decay or other oral health issues, reducing the risk of dental abscesses.
Teaching children proper brushing and flossing techniques and ensuring they practice them consistently can minimize the chance of tooth decay and subsequent abscesses. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks can also help prevent dental decay and reduce the risk of abscesses. Using fluoride toothpaste and receiving professional fluoride treatments can strengthen tooth enamel and decrease the likelihood of tooth decay.
