Smoking and its Impact on Oral Health
Smoking can have serious consequences on oral health, leading to various dental and oral problems. One of the most common effects is tooth discoloration. The nicotine and tar present in cigarettes can stain the teeth, causing them to become yellow or brown over time. Additionally, smoking can contribute to bad breath, as it causes a dry mouth, decreases saliva production, and promotes the growth of bacteria in the mouth.
Importance of Discussing Oral Health Risks Associated with Smoking
It is crucial to discuss the oral health risks associated with smoking because awareness and education can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Many smokers may not be aware of the specific oral health consequences they face, and by providing this information, dental professionals and healthcare providers can encourage them to quit smoking or seek appropriate treatment.
By discussing the oral health risks, healthcare professionals can also help smokers understand the importance of regular dental check-ups and oral hygiene practices. These preventive measures, such as professional cleanings, can help mitigate the damage caused by smoking and detect any issues early on.
Stained Teeth and Bad Breath

Effects of smoking on teeth discoloration
Smoking has a profound impact on the appearance of teeth, causing a significant discoloration that can be difficult to reverse. The nicotine and tar present in cigarettes are notorious for staining teeth, resulting in a yellow or brownish hue over time. These substances have a tendency to accumulate on the enamel, creating a stubborn layer of discoloration that regular brushing and dental hygiene practices alone may not be able to remove. As a result, smokers often find themselves with a smile that lacks the brightness and whiteness they desire.
How smoking contributes to bad breath
In addition to teeth discoloration, smoking also contributes to the problem of bad breath. When you smoke, the chemicals in cigarettes cause a decrease in saliva production, resulting in a dry mouth. Saliva plays a crucial role in washing away food particles and bacteria from the mouth, so a decrease in saliva allows bacteria to thrive and produce unpleasant odors. Furthermore, smoking itself can leave a distinct and unfavorable smell on the breath that is difficult to mask with typical oral hygiene practices such as mouthwash or mints.
Moreover, smoking irritates the gums and affects the overall health of the oral cavity, leading to an increased risk of gum disease. The toxins in cigarette smoke weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. This weakened defense leaves the gums vulnerable to inflammation, leading to gingivitis and, if left untreated, more severe periodontal disease. Chronic gum disease can cause persistent bad breath, as well as other oral health issues such as gum recession, tooth loss, and bone damage.
Gum Disease
Link between smoking and gum disease
Smoking not only affects the appearance of teeth but also has a detrimental impact on oral health. One of the most serious consequences of smoking is an increased risk of gum disease. Studies have shown that smokers are two to three times more likely to develop gum disease compared to non-smokers. The chemicals present in cigarettes, such as nicotine and tar, not only stain teeth but also irritate the gums, making them more susceptible to infection and inflammation.
When a person smokes, the toxins in cigarette smoke suppress the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. As a result, the gums become more vulnerable to bacteria, leading to the development of gum disease. Additionally, smoking hampers blood flow to the gums, which further impairs the body’s ability to heal and fight off infections in the oral cavity.
Increased risk of periodontal disease due to smoking
Smoking significantly increases the risk of periodontal disease, a severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and other serious oral health problems. Periodontal disease occurs when the infection and inflammation of the gums spread to the surrounding tissues and bone that support the teeth. Smoking exacerbates this condition by hampering the healing process and weakening the immune system.
Research has found that smokers with periodontal disease experience more bone loss and have a higher risk of tooth loss compared to non-smokers with the same condition. The toxins in cigarette smoke not only impair the body’s ability to repair damaged tissue but also increase the production of harmful bacteria in the oral cavity.
It is important for smokers to be aware of the increased risk of gum disease and periodontal disease associated with smoking. Quitting smoking is crucial not only for overall health but also for maintaining a healthy and disease-free mouth. Seeking professional dental care, practicing good oral hygiene, and regularly visiting the dentist can help mitigate the effects of smoking on oral health and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Oral Cancer
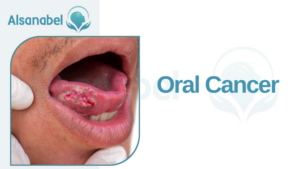
Smoking as a major risk factor for oral cancer
Smoking is not just harmful to overall health, it is also a major risk factor for oral cancer. The chemicals present in cigarettes, such as carcinogens, increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer. When a person smokes, these harmful substances are absorbed by the oral tissues, leading to genetic mutations and the growth of abnormal cells.
Tobacco smoke contains thousands of chemicals, including tar, nicotine, and formaldehyde, which are known to cause DNA damage and impair the body’s ability to repair itself. The constant exposure to these toxic substances increases the risk of oral cancer significantly.
Statistics and prevalence of oral cancer among smokers
Studies have shown a strong connection between smoking and oral cancer. Smokers are six times more likely to develop oral cancer compared to non-smokers. In fact, around 90% of people with oral cancer have a history of tobacco use.
According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 48,330 new cases of oral cavity and pharynx cancer were diagnosed in the United States in 2021. Of these cases, a significant portion can be directly attributed to smoking. The prevalence of oral cancer among smokers is alarmingly high, highlighting the urgent need for smoking cessation.
Tooth Loss
Relationship between Smoking and Tooth Loss
Smoking not only poses a threat to overall health but also has a detrimental effect on oral health. One of the consequences of smoking is an increased risk of tooth loss. Numerous studies have shown a clear relationship between smoking and tooth loss, with smokers being more likely to experience dental problems compared to non-smokers. In fact, research suggests that smokers are twice as likely to lose their teeth compared to non-smokers.
Impact of Smoking on Gum and Bone Health leading to Tooth Loss
The impact of smoking on tooth loss can be attributed to its negative effects on gum and bone health. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke impair the blood flow to the gums, making it harder for infected gums to heal. Consequently, smokers are more susceptible to gum disease, which is one of the leading causes of tooth loss.
Smoking also affects the bone structure that supports the teeth. It disrupts the normal bone remodeling process, leading to a decrease in bone density and ultimately resulting in weakened jawbones. This weakened bone structure makes it difficult for the teeth to stay firmly in place, increasing the likelihood of tooth loss.
Additionally, smoking compromises the immune system’s ability to fight infections, further exacerbating oral health problems. The combination of compromised immune function, reduced blood flow to the gums, and impaired bone health significantly increases the risk of tooth loss among smokers.
It is important for smokers to be aware of the impact of smoking on oral health and the increased risk of tooth loss. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for overall health but also plays a crucial role in preserving oral health and preventing tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle are essential in maintaining a strong foundation for teeth and gums.
Reduced Effectiveness of Treatment
How smoking compromises the success of dental treatments
Smoking not only has a detrimental effect on overall health and tooth loss but also significantly compromises the effectiveness of various dental treatments. The chemicals present in cigarette smoke can interfere with the healing process and reduce the success rate of dental procedures. Here’s how smoking impacts the effectiveness of common dental treatments:
- Implants and Surgeries: Dental implants, which are artificial tooth roots, provide a long-lasting solution for missing teeth. However, smoking can hinder the success of dental implant procedures. The chemicals in cigarettes affect blood circulation and can impede the integration of the implant with the jawbone, leading to a higher risk of implant failure. Smokers are at a greater risk of experiencing complications such as implants not fusing properly or developing infections.
- Root Canal Treatment: Root canal treatment is performed to save an infected or damaged tooth. However, smoking can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of post-treatment complications. The chemicals in cigarette smoke compromise blood flow to the treated tooth, making it difficult for the surrounding tissues to heal. This can result in persistent pain, reinfection, or even the need for extraction.
- Gum Disease Treatment: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease, and it can also hinder the success of gum disease treatments. The chemicals in cigarettes weaken the gum tissues, making them more susceptible to infection and slower to heal. Smoking reduces the effectiveness of treatments such as scaling and root planing, gum surgery, and antibiotic therapy, leading to a higher chance of disease progression and tooth loss.
Challenges faced by dental professionals in treating smokers
Dental professionals face unique challenges when treating patients who smoke. These challenges include:
- Delayed Healing: Smokers usually experience delayed wound healing due to the reduced blood flow to the tissues. This delays the recovery process after dental procedures and increases the risk of complications.
- Increased Infection Risk: Smoking compromises the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to infections. This poses challenges in managing oral infections, such as gum disease or abscesses, and increases the risk of treatment failure.
- Limited Treatment Options: In certain cases, smoking can limit the available treatment options. For example, some dental procedures, like bone grafting, may not be as successful in smokers due to impaired bone healing.
Dental professionals advocate for smoking cessation to improve treatment outcomes and overall oral health. Quitting smoking enhances the body’s ability to heal, reduces infection risks, and increases the success rates of dental treatments. Dental professionals also play a crucial role in educating and supporting patients in their journey to quit smoking.
Secondhand Smoke and Oral Health

Negative effects of secondhand smoke on oral health
Secondhand smoke, also known as passive smoking, refers to the inhalation of tobacco smoke from the burning end of a cigarette or the smoke exhaled by a smoker. This can have significant detrimental effects on oral health. Here are some of the negative impacts of secondhand smoke on oral health:
- Increased risk of gum disease: Secondhand smoke contains harmful chemicals that can weaken gum tissues and increase the risk of gum disease. Being exposed to secondhand smoke regularly can lead to inflamed gums, bad breath, and eventually, gum disease.
- Impaired healing: The chemicals in secondhand smoke can interfere with the body’s natural healing process. This can be particularly problematic after dental procedures such as extractions or gum surgeries. Secondhand smoke exposure can slow down the healing of wounds in the mouth, leading to potential complications.
- Cavities and tooth decay: Secondhand smoke can also contribute to the development of cavities and tooth decay. The harmful chemicals present in the smoke can weaken tooth enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay. Additionally, the presence of smoke particles in the mouth can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth and plaque formation.
Protecting oral health in environments with smokers
While it may be challenging to control exposure to secondhand smoke in certain environments, there are steps that individuals can take to protect their oral health:
- Avoidance: Whenever possible, try to avoid being in close proximity to smokers or in areas where smoking is allowed. This includes both indoor and outdoor environments. Limiting exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce its negative effects on oral health.
- Oral hygiene: Practicing good oral hygiene is crucial in maintaining optimal oral health, especially in environments with smokers. Brushing twice a day, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash can help remove any harmful smoke particles and reduce the risk of oral health problems.
- Regular dental check-ups: Regular visits to the dentist are essential for monitoring and maintaining oral health. Dentists can assess the impact of secondhand smoke on oral health and provide appropriate treatment or advice to mitigate any potential damage.
Importance of Quitting Smoking for Oral Health
Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining good oral health. By quitting, individuals can reduce their exposure to harmful chemicals and minimize the risk of developing gum disease. Smoking cessation also improves the healing process, ensuring that dental procedures can be carried out effectively and without complications. Moreover, quitting smoking decreases the chances of developing cavities and tooth decay, as the harmful smoke particles no longer weaken tooth enamel and promote bacterial growth.
Resources and Strategies to Quit Smoking and Improve Oral Health
There are various resources and strategies available to help individuals quit smoking and improve their oral health. Here are some recommendations:
- Seek professional help: Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide the necessary guidance and support to quit smoking. They can recommend nicotine replacement therapy, medications, or counseling programs tailored to one’s needs.
- Join support groups: Connecting with others who are also trying to quit smoking can provide valuable support and motivation. Support groups, both online and in-person, offer a sense of community and shared experiences.
- Practice healthy coping mechanisms: Smoking often serves as a coping mechanism for stress. Finding alternative ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies, can reduce the urge to smoke and improve overall well-being.
- Utilize oral health products: Using oral health products specifically designed for smokers, such as nicotine-free gum or toothpaste, can help transition away from smoking and protect oral health.
- Create a smoke-free environment: Removing smoking triggers from the surrounding environment can make quitting easier. This may involve avoiding social situations where smoking is prevalent or asking family members and friends to refrain from smoking in shared spaces.
Remember, protecting oral health is crucial, and taking the necessary steps to quit smoking will not only benefit your oral health but also your overall well-being. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help and utilize available resources in your journey towards a smoke-free life.
