Dental Emergencies
Dental emergencies can occur at any time and can range from mild to severe. It is important to be able to recognize these emergencies to seek timely treatment. Some of the common dental emergencies include:
- Toothache: Severe toothache can indicate an abscess or decay. It is important to seek dental attention as soon as possible to alleviate the pain and prevent further damage.
- Broken or chipped tooth: A broken or chipped tooth can cause pain and increase the risk of infection. Prompt treatment can help restore the tooth’s function and aesthetics.
- Knocked-out tooth: If a tooth gets completely knocked out, it is crucial to preserve the tooth and seek immediate dental care. The chances of saving the tooth increase if it is placed back in the socket within an hour.
- Lost filling or crown: When a filling or crown falls out, the affected tooth becomes vulnerable to damage and decay. It is important to visit a dentist promptly to replace the filling or crown and protect the tooth.
Importance of understanding dental emergencies
Understanding dental emergencies is crucial for several reasons:
- Timely treatment: Prompt action can help prevent further damage, alleviate pain, and increase the chances of saving the tooth. Being aware of dental emergencies enables individuals to seek immediate treatment.
- Prevent complications: Dental emergencies, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications such as infections, tooth loss, and gum disease. Understanding these emergencies helps individuals take necessary precautions to prevent complications.
- Peace of mind: Knowing how to handle a dental emergency can provide peace of mind, especially in situations where immediate professional help may not be available. It allows individuals to take appropriate temporary measures until they can see a dentist.
In conclusion, being educated about common dental emergencies is essential. Recognizing the signs and symptoms can help individuals seek immediate treatment, prevent complications, and ensure better oral health. It is recommended to consult a dentist for further guidance on dental emergencies and to develop a tailored emergency plan.
Toothache
A toothache can have several underlying causes, including:

- Decay: Tooth decay is one of the leading causes of toothaches. When the outer layer of the tooth, known as enamel, is damaged or eroded, it exposes the sensitive inner layers, causing pain.
- Abscess: An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms at the root of a tooth due to an infection. This can result in severe toothache and swelling.
- Gum disease: Advanced gum disease, also known as periodontitis, can cause toothaches. The infection spreads from the gum tissue to the supporting bone, leading to tooth pain.
- Cracked tooth: A cracked tooth can cause intermittent or constant toothache, depending on the severity of the crack. The pain may worsen when chewing or applying pressure to the affected tooth.
Home remedies for temporary relief
While it is important to seek professional dental care for a toothache, there are a few home remedies that can provide temporary relief:
- Rinse with saltwater: Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and use it to rinse your mouth. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Apply a cold compress: Placing a cold compress on the affected area can help numb the pain and reduce swelling. Wrap an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables in a cloth and apply it to the outside of your cheek near the painful tooth.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help relieve toothache pain and reduce inflammation. Follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
- Clove oil: Clove oil has natural numbing properties and can provide temporary pain relief. Dip a cotton ball in clove oil and apply it to the affected area for a few minutes.
Remember, these home remedies are not a substitute for professional dental care. It is important to schedule an appointment with a dentist to identify and address the underlying cause of the toothache. Ignoring the pain or relying solely on home remedies may lead to further complications.
Knocked-Out Tooth
When a tooth is knocked out, it is important to act quickly to increase the chances of saving the tooth. Here are the immediate steps to take:
- Find the tooth: Locate the knocked-out tooth and handle it carefully by the crown (the visible part) without touching the root.
- Rinse the tooth: Gently rinse the tooth with water to remove any dirt or debris, but do not scrub or use soap.
- Reinsert the tooth (if possible): If the tooth is still clean and undamaged, try to reinsert it into the socket. Hold it in place by gently biting down on a clean cloth or gauze.
- Keep the tooth moist: If reinserting the tooth is not possible, keep it moist to prevent it from drying out. Place it in a container with milk, saliva, or a saline solution. Avoid using water as it can damage the root cells.
- Seek immediate dental care: Contact a dentist or emergency dental clinic as soon as possible. Time is crucial in saving a knocked-out tooth, so it is important to seek professional help without delay.
How to handle a knocked-out tooth
Here are some important things to keep in mind when handling a knocked-out tooth:
- Do not touch the root: Handle the tooth only by the crown to avoid damaging the fragile root surface.
- Avoid scrubbing or wiping: Do not scrub or wipe the tooth, as it may remove important tissues needed for successful reattachment.
- Do not let the tooth dry out: It is crucial to keep the tooth moist to increase the chances of saving it. Store it in milk, saliva, or a saline solution until you can see a dentist.
- Do not use medication or chemicals: Avoid using any medication, alcohol, or chemicals on the tooth, as they may harm the root surface.
Remember, a knocked-out tooth requires immediate dental attention. The steps mentioned above are meant to provide temporary care until you can reach a dental professional. Dental re-implantation within the first hour has the highest success rate, so time is of the essence.
Dental Abscess
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms within the teeth, gums, or surrounding tissues. It develops as a result of a bacterial infection, usually originating from tooth decay or a dental injury. The abscess can cause severe pain and swelling in the affected area.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a dental abscess may include:
- Toothache: A persistent, throbbing pain in the affected tooth is a common symptom of a dental abscess.
- Swelling: The area around the infected tooth may become swollen and tender.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may be experienced in the affected tooth or surrounding area.
- Gum inflammation: The gums near the affected tooth may appear red, swollen, and may bleed easily.
- Bad breath or bitter taste: A foul odor or unpleasant taste in the mouth may be present due to the presence of pus.
- Difficulty chewing or biting: Pain or discomfort while biting down or chewing may be experienced due to the abscess.
- Fever: In some cases, a dental abscess may be accompanied by a low-grade fever.
If you suspect you have a dental abscess, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. A dental professional can diagnose the condition through a visual examination and may recommend further tests such as an X-ray to determine the extent of the infection.
Broken or Chipped Tooth
A broken or chipped tooth can occur due to several reasons, including:
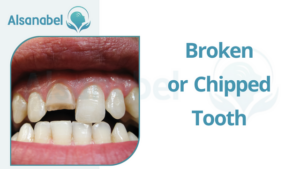
- Trauma: Accidents or injuries to the mouth, such as falls or sports-related incidents, can lead to a broken or chipped tooth.
- Biting down on hard objects: Chewing on hard candies, ice, or pens can put excessive pressure on the teeth and cause them to chip or break.
- Tooth decay: Weakened teeth due to decay are more prone to breaking.
- Teeth grinding: The habit of grinding or clenching the teeth, especially during sleep, can cause teeth to become weak and eventually chip or break.
Treatment options
The treatment options for a broken or chipped tooth depend on the severity of the damage. Here are some common treatment options:
- Dental bonding: In cases where only a small portion of the tooth is chipped, dental bonding can be used to reshape and restore the tooth. The dentist will apply a tooth-colored resin to the affected area, which is then hardened and polished to match the natural tooth.
- Dental crowns: If a large portion of the tooth has broken off or if the tooth is severely damaged, a dental crown may be recommended. A crown is a custom-made cap that covers the entire tooth, providing strength and protection.
- Dental veneers: Veneers are thin, custom-made shells that are bonded to the front surface of the teeth. They can be used to restore the appearance of chipped or broken teeth, providing a natural and aesthetically pleasing result.
- Root canal: In cases where the tooth pulp is exposed or damaged, a root canal procedure may be necessary. This involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection.
It is important to seek prompt dental care if you have a broken or chipped tooth, as untreated damage can lead to further complications, such as tooth infections or tooth loss. A dentist will assess the extent of the damage and recommend the most appropriate treatment option to restore the tooth’s appearance and function. Remember to practice good oral hygiene and avoid habits that can increase the risk of tooth damage.
Lost Filling or Crown
A lost filling or crown can occur due to several reasons, including:
- Decay: If tooth decay is not treated promptly, it can weaken the tooth structure, causing a filling or crown to become loose or fall out.
- Wear and tear: Over time, fillings and crowns can become worn or loosened due to normal chewing and biting forces.
- Trauma: A sudden impact or injury to the mouth can dislodge a filling or crown.
- Sticky foods: Consuming sticky or chewy foods can sometimes pull out a filling or crown.
Temporary solutions until dental visit
If you experience a lost filling or crown, it is important to schedule a dental visit as soon as possible. In the meantime, there are temporary solutions you can try:
- Dental cement: Over-the-counter dental cement can be used to temporarily reattach a loose crown or filling. Follow the instructions carefully and avoid chewing on the affected tooth.
- Dental wax: If a crown or filling has fallen out completely, you can use dental wax to cover the exposed area and protect it from sensitivity or further damage.
- Avoid hard or sticky foods: Until you can see a dentist, it’s best to avoid eating hard or sticky foods that could potentially further dislodge the filling or crown.
Remember, these temporary solutions are meant to provide temporary relief and should not replace professional dental care. It is important to see a dentist promptly to address the issue and ensure the filling or crown is properly replaced or repaired.
Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries refer to damage or trauma to the skin, muscles, ligaments, or tendons. There are different types of soft tissue injuries, including:
- Abrasions: These are superficial injuries that result from scraping or rubbing the skin against a rough surface, causing a scrape or graze.
- Contusions: Also known as bruises, contusions occur when blood vessels under the skin rupture, leading to discoloration and pain.
- Sprains: Sprains happen when ligaments, which connect bones to each other, are stretched or torn due to sudden twisting or impact. This can cause pain, swelling, and decreased range of motion.
- Strains: Strains occur when muscles or tendons are stretched or torn. Common causes include overuse, improper lifting techniques, or sudden movements.
First aid for soft tissue injuries
Applying proper first aid can help alleviate pain and promote healing for soft tissue injuries. Here are some steps to take:
- Rest: Immediately stop the activity that caused the injury and avoid putting weight or strain on the affected area.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the injured area. This can help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. Apply it for about 10 to 20 minutes at a time, with breaks in between.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage or wrap to reduce swelling. Ensure that it is snug but not too tight, as this can impair circulation.
- Elevation: Raise the injured part above the level of the heart to reduce swelling. Use pillows or cushions for support.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain medication can be taken, following the recommended dosage, to relieve pain and discomfort.
If the injury is severe or does not improve within a few days, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as physical therapy or surgery.
Jaw/Tooth Fracture
A jaw/tooth fracture can be a painful and serious injury. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms to take appropriate action. Common signs and symptoms of a jaw/tooth fracture include:
- Severe pain in the jaw or tooth area
- Difficulty or inability to open the mouth fully
- Misalignment of the jaw or teeth
- Bruising or swelling around the jaw or face
- Bleeding from the mouth
- Loose, broken, or missing teeth
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Immediate actions to take
In the event of a suspected jaw/tooth fracture, there are some immediate actions you can take to help manage the situation until medical help arrives:
- Stabilize the jaw: To prevent further damage, support the jaw by gently holding it in place. You can use your hand or a cloth to provide support.
- Control bleeding: If there is bleeding from the mouth, gently rinse with water and apply pressure to stop the bleeding. Be careful not to disturb any loose or broken teeth.
- Apply cold compress: To reduce swelling and alleviate pain, apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the affected area. Apply it for about 10 to 20 minutes at a time, with breaks in between.
- Avoid eating or chewing: Refrain from eating or chewing until you receive medical attention. This will help minimize further damage to the jaw or teeth.
- Seek dental or medical assistance: Contact a dentist or visit the nearest emergency room as soon as possible to receive proper medical care.
It’s important to remember that a jaw/tooth fracture requires immediate attention from a medical professional. They will be able to assess the extent of the injury and provide appropriate treatment options, which may include splinting the jaw, dental repairs, or surgical intervention.
Importance of seeking professional help
It is crucial to seek professional medical help in the case of a jaw/tooth fracture. Prompt medical attention is necessary to properly diagnose the extent of the injury and provide appropriate treatment options. Ignoring or delaying treatment can lead to further complications and prolonged pain.

Only a medical professional will be able to assess the fracture accurately and determine the best course of action, which may include splinting the jaw, dental repairs, or surgical intervention. Do not attempt to handle a jaw/tooth fracture on your own without the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Tips for preventing dental emergencies
While accidents can happen, there are measures you can take to reduce the risk of dental emergencies. Here are some tips:
- Avoid chewing hard objects: Do not bite or chew on hard objects like ice, unpopped popcorn kernels, or pen caps. These can cause tooth fractures or damage to dental restorations.
- Wear a mouthguard during sports activities: If you participate in contact sports or activities with a risk of facial trauma, use a properly fitted mouthguard to protect your teeth and jaw.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help detect and prevent dental issues that may lead to emergencies.
- Avoid biting or chewing on non-food items: Resist the urge to use your teeth as tools to open packages or bite off clothing tags. These activities can result in tooth fractures or damage to your teeth and gums.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Eating a healthy diet that includes calcium-rich foods can help strengthen your teeth and reduce the risk of dental problems.
By following these preventive measures and staying mindful of your oral health, you can minimize the chances of encountering dental emergencies, including jaw/tooth fractures.
Remember, only a medical professional can properly assess and treat a jaw/tooth fracture. Seeking prompt medical attention is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, taking preventive measures, such as avoiding chewing hard objects, wearing a mouthguard during sports, practicing good oral hygiene, and maintaining a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of dental emergencies.
