Dental Surgeries
Dental surgery encompasses a wide range of medical procedures that involve the modification of dentition, including the teeth, gums, and jaw. These surgeries are typically performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons or periodontists, who are dental specialists trained in oral surgery procedures.
Why dental surgeries are necessary
There are several reasons why dental surgeries may be necessary. One of the most common types of oral surgery is tooth extraction, which is recommended in cases of severe tooth decay, gum disease, dental trauma, or complications related to wisdom teeth. Extractions may also be performed to prepare the mouth for the placement of dental implants or other prosthetic devices. Oral surgeries can also address issues such as gum grafts, periodontal surgery for gum disease treatment, corrective jaw surgery, sleep apnea surgery, and cleft lip and palate repair.
Gum grafts are often done to treat receding gums and prevent further gum recession, while periodontal surgery helps to treat advanced gum disease and prevent tooth loss. Corrective jaw surgery is performed to correct misaligned jaws or treat conditions such as TMJ disorders. Sleep apnea surgery aims to improve airflow and alleviate symptoms of sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. Cleft lip and palate repair surgeries are necessary to correct congenital defects in the mouth and facial structures.
Extractions

Simple tooth extractions
Simple tooth extractions are the most common type of dental extraction performed by dentists. They involve the removal of teeth that are visible and easily accessible. These extractions are typically done under local anesthesia to numb the area around the tooth.
During a simple tooth extraction, the dentist uses a dental tool called an elevator to loosen the tooth and then uses forceps to gently extract it from its socket. The extraction process is relatively quick and straightforward, usually lasting only a few minutes.
After the tooth is removed, the dentist will place a gauze pad on the extraction site to control bleeding and promote blood clot formation. The patient will be given instructions on how to care for the extraction site and manage any discomfort or swelling. Full recovery from a simple extraction usually takes about one to two weeks.
Surgical tooth extractions
Surgical tooth extractions are more complex and invasive compared to simple extractions. They are typically performed when a tooth is impacted, meaning it is not fully erupted or is stuck in the gum or jawbone. Surgical extractions may also be necessary for removing tooth roots left behind after a previous extraction.
During a surgical extraction, the oral and maxillofacial surgeon or periodontist may need to make an incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth. In some cases, a small portion of the surrounding bone may also need to be removed to fully extract the tooth. This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia or sedation to ensure the patient’s comfort.
Recovery from surgical extractions may take longer than simple extractions, with some discomfort and swelling expected for several days. The dentist will provide post-operative instructions, including pain management techniques and proper oral hygiene practices.
Dental implants
Dental implant surgery is a procedure that involves replacing tooth roots with metal screw-like posts and replacing damaged or missing teeth with artificial teeth that look and function like real ones. Dental implants provide a long-lasting and natural-looking solution for individuals with missing teeth.
Stages of dental implant surgery
Dental implant surgery typically involves several stages.
- The first stage is the initial consultation and examination, during which the dentist or oral surgeon will assess the patient’s oral health and determine if they are a suitable candidate for dental implants.
- The second stage involves the placement of the dental implant. This is done during a surgical procedure, where the implant is inserted into the jawbone.
- After the implant placement, a healing period is necessary to allow the implant to integrate with the surrounding bone. This process typically takes several months.
- Once the implant has fully integrated, the next stage involves attaching an abutment to the implant. The abutment serves as a connector between the implant and the artificial tooth.
- The final stage of dental implant surgery is the placement of the dental crown. The crown is custom-made to match the color, shape, and size of the patient’s natural teeth, providing a natural and functional tooth replacement.
It’s important to note that the exact stages and timeline of dental implant surgery may vary depending on the individual case and the patient’s overall oral health. It is crucial to consult with a dental professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
Root Canal Treatment
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontic treatment, is a dental procedure that is performed to relieve pain caused by an infected or abscessed tooth. It involves removing the infected pulp from the inner part of the tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the root canals, and then sealing them to prevent further infection. This treatment is necessary when the pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels, becomes infected due to deep decay, a cracked tooth, or trauma to the tooth.
During the root canal procedure, the dentist or endodontist will start by numbing the area around the affected tooth using a local anesthetic. They will then create a small access hole in the tooth to reach the infected pulp. The infected pulp, along with any debris or bacteria, is carefully removed using specialized tools. Once the canals are cleaned, they are shaped to create space for filling material. The canals are then filled with a rubber-like material called gutta-percha, and the access hole is sealed with a temporary filling.
Procedure and Aftercare for Root Canal Surgery
After the root canal treatment, the patient may experience some sensitivity or discomfort, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. It is important to avoid chewing on the treated tooth until the permanent restoration, such as a dental crown, is placed to protect the tooth from further damage.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, is essential for the long-term success of the root canal treatment. Regular check-ups with the dentist will also help ensure the tooth is healing properly.
In some cases, additional procedures may be needed after the root canal treatment, such as placing a dental crown or performing a dental implant to restore the tooth’s functionality and appearance.
Root canal treatment is a highly successful procedure that can save a tooth from extraction and alleviate pain caused by infection. It is important to consult with a qualified dentist or endodontist to determine if root canal treatment is the best option for your specific dental condition.
Wisdom teeth removal
While it is common to grow a set of four wisdom teeth, some people may only grow a couple, while others may not grow any wisdom teeth at all. Wisdom tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that may be necessary for various reasons. One common reason for wisdom teeth removal is when they become impacted, meaning they are unable to fully emerge from the gumline. This can lead to pain, swelling, and an increased risk of infection.
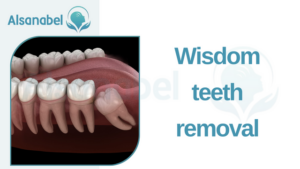
Another common reason for wisdom teeth removal is overcrowding. If there is not enough space in the mouth to accommodate the wisdom teeth, they may come in at an angle or push against other teeth, causing misalignment and potential damage to neighboring teeth.
In some cases, wisdom teeth may only partially erupt, leaving a flap of gum tissue that can trap food and bacteria, leading to infection and decay. Additionally, wisdom teeth that are located in a difficult-to-reach area may make proper oral hygiene challenging, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Surgical and non-surgical methods for extraction
There are two types of wisdom tooth extraction—simple and surgical. If the wisdom tooth is visible and fully erupted, a simple dental extraction can be performed. This involves numbing the area with local anesthesia and using dental tools to loosen and remove the tooth.
On the other hand, if the wisdom tooth is impacted or difficult to access, surgical extraction may be necessary. In this case, the dentist or oral surgeon will make a small incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth. Depending on the complexity of the extraction, the tooth may need to be divided into multiple pieces before being removed.
Surgical extraction may require the use of general anesthesia or intravenous sedation to ensure the patient’s comfort throughout the procedure. The dentist or oral surgeon will provide detailed instructions for post-operative care, which may include pain management, swelling reduction, and proper oral hygiene practices.
It is important to consult with a dental professional to determine the best method of extraction based on the unique circumstances of each individual case. They will carefully evaluate the position and condition of the wisdom teeth to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
gum surgeries
When it comes to gum surgeries, there are several types that serve different purposes.
- One common type is gingival flap surgery, which is often used to treat gum disease. This procedure involves lifting the gums away from the teeth to expose and clean the root surfaces. It can also be used for cosmetic purposes to improve the appearance of teeth when the gums cover too much of them, also known as a gummy smile.
- Another type of gum surgery is gingivectomy, which involves removing excess gum tissue. This is often done to reduce the pocket depth and improve access for proper oral hygiene. It can also be done for aesthetic reasons to create a more balanced and symmetrical smile.
- Gingivoplasty is a similar procedure to gingivectomy, but instead of removing gum tissue, it reshapes the gum line to improve its appearance. This procedure is often used to correct uneven gum levels and create a more harmonious smile.
- In some cases, a gum graft may be needed. This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth, such as the palate, and attaching it to the area with gum recession. This helps to cover exposed root surfaces and prevent further damage.
Recovery and post-operative care for gum surgeries
After gum surgery, it is important to take proper care of your oral health to ensure a smooth recovery. Your dentist or periodontist will provide specific instructions, but here are some general guidelines to follow.
- Take prescribed medications as directed to manage any discomfort or reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid strenuous activities and follow a soft or liquid diet for the first few days.
- Be gentle with brushing and flossing in the treated area, and use a mouthwash recommended by your dentist.
- Avoid smoking and consuming alcohol, as these can hinder the healing process.
- Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and receive any necessary post-operative care.
It is worth mentioning that each patient’s recovery process may vary depending on the type of gum surgery performed and their overall oral health. It’s important to consult with your dentist or periodontist for personalized advice and to address any concerns you may have.
Remember, undergoing gum surgery not only improves the health of your gums but can also enhance the appearance of your smile. So, if you are experiencing gum-related issues, consult with a dental professional who specializes in gum treatments to explore your options and determine the best course of action.
Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery, also known as jaw surgery, is a surgical procedure performed by maxillofacial or oral surgeons, as well as plastic surgeons, in collaboration with orthodontists. It is done to correct misalignments or abnormalities in the upper jaw (maxilla) and/or lower jaw (mandible) that can affect the function and appearance of the face.
The main goal of orthognathic surgery is to achieve proper alignment and function of the maxillo-mandibular complex. This surgical intervention is often recommended for individuals with conditions such as malocclusion (poor bite), skeletal discrepancies, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or sleep apnea.
Misalignments in the jaw can cause difficulties in speaking, chewing, breathing, and even sleeping. Orthognathic surgery aims to improve these functions and restore balance to the facial features.
Different types of orthognathic surgery procedures
There are different types of orthognathic surgery procedures, and the specific procedure depends on the individual’s needs and the extent of the misalignment. Some common types of orthognathic surgery include:
- Maxillary Osteotomy: This procedure focuses on adjusting the position of the upper jaw. It may involve moving the jaw forward, backward, upward, or downward to achieve proper alignment.
- Mandibular Osteotomy: This procedure is performed on the lower jaw to correct its position. It may involve moving the jaw forward or backward to align it with the upper jaw.
- Genioplasty: Also known as chin surgery, genioplasty involves reshaping the chin to improve facial balance and aesthetics. It can be performed in conjunction with other orthognathic procedures or as a standalone procedure.
- Bimaxillary Osteotomy: In cases where both the upper and lower jaws need adjustment, a bimaxillary osteotomy is performed. This procedure involves realigning both jaws to achieve proper function and aesthetics.
Orthognathic surgery often requires the use of braces before and after the procedure to ensure the correct alignment of the teeth. It is important to consult with a qualified oral surgeon and orthodontist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and understand the potential risks and benefits of the procedure.
Periodontal Surgeries
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common oral condition that affects the gums, tissues surrounding the teeth, and even the jawbone. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious complications. In some cases, non-surgical treatments such as scaling and root planing may be sufficient to manage the disease. However, in more advanced cases, periodontal surgeries may be necessary.
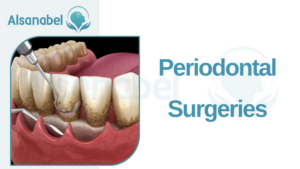
There are three primary types of periodontal surgery used to repair and treat gum disease:
- Gingival Flap Surgery: This type of surgery involves creating a small incision in the gum tissue to lift the gums and gain access to the roots of the teeth. The dentist or periodontist can then remove plaque, tartar, and infected tissue, and perform any necessary bone grafting. The gums are then repositioned and sutured back in place to promote healing.
- Mucogingival Surgery: Mucogingival surgery focuses on correcting gum and soft tissue defects caused by gum recession. During this procedure, the periodontist takes a graft of gum tissue from another part of the mouth or uses a synthetic material to cover the exposed root surfaces. This helps to protect the roots, reduce sensitivity, and enhance the aesthetic appearance of the gums.
- Osseous Surgery: Osseous surgery, also known as pocket depth reduction surgery, involves reshaping and smoothing the damaged bone around the teeth affected by gum disease. The periodontist removes any infected tissue, eliminates irregular tooth surfaces, and recontours the jawbone to eliminate deep gum pockets. This procedure is crucial in preventing the progression of gum disease and promoting better oral health.
Treatment options and expected outcomes
The choice of periodontal surgery depends on the severity of the gum disease and the specific needs of the individual. Your dentist or periodontist will evaluate your condition and recommend the most appropriate surgery for optimal results.
Periodontal surgery aims to restore healthy gum tissue, reduce pocket depth, and promote proper gum attachment to the teeth. By eliminating infection and repairing damaged tissues, patients can experience improved oral health, enhanced aesthetics, and a reduced risk of tooth loss.
It is important to follow post-surgical instructions carefully to ensure proper healing and maintain the results achieved through periodontal surgery. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, are essential for long-term success.
If you are experiencing gum disease or have concerns about your periodontal health, consult with a qualified dentist or periodontist to discuss your treatment options and determine if periodontal surgery is necessary in your case.
Importance of dental surgeries
In conclusion, dental surgeries play a crucial role in maintaining oral health and preventing the progression of various dental conditions. These surgeries are often necessary when non-surgical treatments are not sufficient to address the problem. The three common types of dental surgeries explained include periodontal surgeries for gum disease, which are Gingival Flap Surgery, Mucogingival Surgery, and Osseous Surgery.
Gingival Flap Surgery involves lifting the gums to access the roots of the teeth and remove plaque, tartar, and infected tissue. This procedure promotes healing and prevents tooth loss. Mucogingival Surgery focuses on correcting gum recession by grafting gum tissue from another part of the mouth or using synthetic materials. This procedure protects the roots, reduces sensitivity, and enhances the appearance of the gums. Osseous Surgery reshapes and smoothes the damaged bone around the teeth affected by gum disease. It eliminates infected tissue and recontours the jawbone to prevent the progression of gum disease.
These surgeries aim to restore healthy gum tissue, reduce pocket depth, and promote proper gum attachment to the teeth. By eliminating infection and repairing damaged tissues, patients can experience improved oral health, enhanced aesthetics, and a reduced risk of tooth loss. However, it is important to note that the choice of surgery depends on the severity of the condition and individual needs, as determined by a qualified dentist or periodontist.
To maintain the results achieved through dental surgery, it is essential to follow post-surgical instructions carefully. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, are also crucial for long-term success.
It is always recommended to consult with a qualified dental professional to discuss personalized advice and treatment options. Dental surgeries should only be performed by trained professionals to ensure safe and effective outcomes. By prioritizing oral health and seeking appropriate dental care, individuals can maintain a healthy smile and overall well-being.
