Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that affects people of all ages. It occurs when the bacteria in your mouth produce acids that attack the enamel, the outer layer of your teeth. If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to cavities, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. However, with proper knowledge and oral hygiene practices, you can prevent tooth decay and maintain good oral health. In this article, we will provide an overview of tooth decay and its impact on oral health, as well as discuss the stages of tooth decay and how to prevent them.
Overview of Tooth Decay and its Impact on Oral Health
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is the most common chronic disease in both children and adults. It can cause pain, discomfort, and negatively impact overall oral health. When you consume sugary foods and drinks, the bacteria in your mouth produce acids that attack the enamel, gradually eroding it and leading to tooth decay.
If left untreated, tooth decay can progress through different stages, starting with the demineralization of the enamel, followed by the development of a cavity or hole in the tooth. If the decay reaches the inner layer of the tooth, called the dentin, it can cause sensitivity and pain. In advanced stages, the decay can reach the pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels, leading to severe pain, infection, and potential tooth loss.
To prevent tooth decay, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Additionally, minimizing the consumption of sugary foods and drinks, along with practicing good dietary habits, can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay.
By understanding the stages of tooth decay and implementing preventive measures, you can ensure good oral health and a bright, healthy smile for years to come.
Stage 1: Initial Demineralization
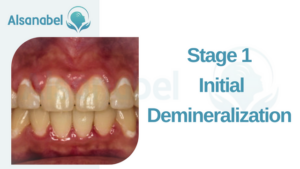
Causes and symptoms of initial demineralization
Initial demineralization is the first stage of tooth decay, where the enamel begins to lose minerals due to acid attacks from bacteria in the mouth. The main cause of this stage is the consumption of sugary foods and drinks, which provide the bacteria with the fuel to produce these acids. Poor oral hygiene practices can also contribute to the formation of plaque, which enhances the acid production and accelerates the demineralization process.
Symptoms of initial demineralization may include white spots or chalky areas on the tooth surface. These spots indicate a loss of minerals and the onset of enamel decay. However, at this stage, there are usually no visible cavities or pain.
Preventive measures for stage 1 decay
To prevent the progression of tooth decay at this stage, it is essential to take proactive measures.
- Brushing and flossing: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the risk of demineralization. Flossing daily also helps remove food particles and plaque from between teeth and along the gum line.
- Fluoride treatment: Using a fluoride mouthwash or toothpaste that is specifically designed to strengthen enamel can help protect against demineralization. Fluoride promotes remineralization and strengthens the teeth.
- Balanced diet: Limiting the intake of sugary foods and drinks is crucial in preventing further acid attacks. Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall oral health.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist regularly allows for early detection and intervention if any signs of initial demineralization or tooth decay are present. Your dentist can provide additional preventive measures such as sealants or fluoride treatments.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can effectively combat initial demineralization and protect your teeth from further decay. Remember, early intervention is key to maintaining optimal oral health and preventing more severe stages of tooth decay.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
Causes and symptoms of enamel decay
Enamel decay is the second stage of tooth decay, where the enamel, the outer protective layer of the tooth, becomes damaged. This is caused by the continued acid attacks from bacteria in the mouth, which break down the enamel over time. The main cause of enamel decay is poor oral hygiene and a diet high in sugars and carbohydrates. Plaque buildup on the teeth also contributes to the acid production and accelerates the decay process.
Symptoms of enamel decay may include visible discoloration of the tooth, increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, and toothache. As the enamel weakens, the tooth becomes more vulnerable to further decay and cavities may start to form.
Preventive measures for stage 2 decay
To prevent the progression of enamel decay and maintain oral health, it is important to take proactive measures.
- Brushing and flossing: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the risk of enamel decay. Flossing daily also helps to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth and along the gum line.
- Fluoride treatment: Using a fluoride mouthwash or toothpaste that is specifically designed to strengthen enamel can help protect against enamel decay. Fluoride promotes remineralization and strengthens the teeth.
- Balanced diet: Limiting the intake of sugary foods and drinks is crucial in preventing the formation of acids that cause enamel decay. Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall oral health.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist regularly allows for early detection and intervention if any signs of enamel decay or cavities are present. Your dentist can provide additional preventive measures such as dental sealants or fluoride treatments.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can effectively combat enamel decay and protect your teeth from further damage. Remember, practicing good oral hygiene and maintaining a healthy diet are essential steps in preventing the progression of tooth decay.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
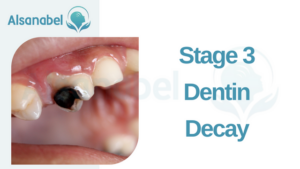
Causes and symptoms of dentin decay
Dentin decay is the third stage of tooth decay and occurs when the decay progresses beyond the enamel and reaches the dentin, which is the layer beneath the enamel. This stage of decay is more serious and can lead to further complications if not addressed promptly.
The main cause of dentin decay is the continued acid attacks from bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acids that break down the enamel and eventually reach the dentin. Poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugars and carbohydrates, and plaque buildup on the teeth contribute to the acid production and accelerate the decay process.
Symptoms of dentin decay may include increased tooth sensitivity, especially when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. Discoloration of the affected tooth and the formation of cavities are also common signs. As the decay progresses, individuals may experience toothache and possible infection if left untreated.
Preventive measures for stage 3 decay
To prevent the progression of dentin decay and maintain oral health, it is crucial to take proactive measures.
- Brushing and flossing: Regular brushing of teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily helps remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the risk of dentin decay. Proper technique and thorough cleaning of all tooth surfaces are essential.
- Fluoride treatment: Using a fluoride mouthwash or toothpaste specifically designed to strengthen enamel and dentin can help protect against decay. Fluoride promotes remineralization and strengthens the teeth.
- Balanced diet: Limiting the intake of sugary foods and drinks is crucial in preventing the formation of acids that cause decay. Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall oral health and provide essential nutrients for strong teeth.
- Regular dental check-ups: Regular visits to the dentist allow for early detection and intervention if any signs of dentin decay or cavities are present. Your dentist can assess the extent of decay and provide necessary treatments such as fillings or dental crowns to restore the affected teeth.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can effectively combat dentin decay and protect their teeth from further damage. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, following a healthy diet, and seeking professional dental care are essential in preventing the progression of tooth decay and maintaining optimal oral health. Remember, prevention is key to preserving your smile and avoiding more serious dental issues down the line.
Different Types of Dental Retainers After Braces 2023
Stage 4: Pulp Infection
Causes and Symptoms of Pulp Infection
Stage 4 of tooth decay is known as pulp infection, which occurs when the decay reaches the innermost part of the tooth, known as the pulp. The pulp contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue, and when it becomes infected, it can cause severe pain and complications if left untreated.
The main cause of pulp infection is the progression of decay from the previous stages. When the enamel and dentin are compromised, bacteria can easily reach the pulp and cause an infection. Additionally, poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugars and carbohydrates, and neglecting regular dental check-ups contribute to the development of pulp infection.
Symptoms of pulp infection include severe toothache, increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks, swelling around the affected tooth, and visible signs of infection such as pus or a bad taste in the mouth. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek immediate dental treatment to prevent further complications, such as abscess formation or the spread of infection to surrounding tissues.
Preventive Measures for Stage 4 Decay
To prevent the development of pulp infection and maintain optimal oral health, it is essential to take proactive measures:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria. Proper technique and thorough cleaning of all tooth surfaces are necessary to prevent decay progression.
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Reduce your intake of sugary foods and beverages, as they contribute to acid formation and bacterial growth. Opt for a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall oral health.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups. Dental professionals can detect early signs of decay and provide necessary treatments to prevent the progression to pulp infection.
- Prompt Treatment: If any signs of decay or infection are present, seek dental treatment promptly. Dentists can provide treatments such as fillings, root canal therapy, or dental crowns to remove the infected pulp and restore the affected tooth.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of pulp infection and maintain optimal oral health. Remember, proactive oral care and regular dental visits are crucial in preventing the progression of tooth decay and protecting the integrity of your smile.
Overall importance of preventative oral care
Preventative oral care plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy smile. Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection of decay and addressing any issues promptly. Alongside dental visits, practicing good oral hygiene at home is crucial.

Individuals should brush their teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste, floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria, and use mouthwash for added protection. It is also important to limit sugary foods and beverages, as they contribute to acid formation and bacterial growth.
Recommended dental hygiene practices
To prevent the development of tooth decay, individuals should follow recommended dental hygiene practices. This includes brushing their teeth with fluoride toothpaste for at least two minutes, ensuring all tooth surfaces are thoroughly cleaned. Flossing should also be done daily to remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and along the gumline. Additionally, individuals should limit their consumption of sugary foods and drinks, opting for a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial for early detection of decay and to receive necessary treatments such as fillings, root canal therapy, or dental crowns.
In conclusion, taking proactive measures in practicing good oral hygiene, maintaining a healthy diet, and visiting the dentist regularly can help individuals prevent the progression of tooth decay and protect the integrity of their smile. By prioritizing preventative oral care, individuals can enjoy long-term oral health and avoid the complications associated with advanced stages of tooth decay.
