Definition and understanding gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation and irritation of the gums. It is usually caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, it can progress to a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis.
The importance of oral health
Maintaining good oral health is crucial for overall well-being. A healthy mouth not only allows you to eat and speak properly but also helps in preventing various oral health problems. Oral health is also closely linked to general health and can affect other parts of the body, such as the heart and lungs. Neglecting oral hygiene can lead to gum disease, tooth decay, and even tooth loss.
Regular brushing and flossing, along with routine dental check-ups, can help prevent gingivitis and other oral health issues. It is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth. Regular dental cleanings can remove any stubborn plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be removed by brushing alone.
Gingivitis and Cardiovascular Health
Researchers have found a strong connection between gum disease and cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that individuals with gum disease have an increased risk of developing heart disease, including conditions such as heart attack and stroke. While the exact mechanisms behind this link are not fully understood, several theories have been proposed.

One theory suggests that the bacteria present in the gums and mouth can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, including the arteries. Once in the arteries, these bacteria can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to the formation of plaques and narrowing of the blood vessels. This can eventually lead to cardiovascular complications.
Inflammatory response and its impact
The inflammatory response plays a significant role in both gum disease and heart disease. In gingivitis, the body’s immune system responds to the presence of bacteria in the gums, causing inflammation. If left untreated, this inflammation can spread to other tissues and structures in the mouth, leading to periodontitis.
Similarly, in cardiovascular disease, inflammation plays a crucial role in the development of plaque formation and the progression of atherosclerosis. Chronic inflammation can contribute to the damage of blood vessel walls and the formation of blood clots, increasing the risk of heart-related events.
It is worth noting that individuals with gum disease often have other risk factors for heart disease, such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise. These factors can further contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
To reduce the risk of gum disease and its potential impact on cardiovascular health, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and routine dental check-ups. Additionally, it is crucial to address other risk factors for heart disease, such as quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
Gingivitis and Respiratory Health
The health of your gums may be more important than you realize when it comes to respiratory health. Research has shown that there is a connection between gum disease and an increased risk of developing respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
One theory behind this link is that the bacteria present in the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to infections. Bacteria that cause gum disease, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, have been found in the respiratory tract of individuals with respiratory infections. These bacteria can thrive in the oral cavity and make their way to the lungs, where they can cause inflammation and infection.
Asthma and periodontal disease connection
Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest a connection between periodontal disease and asthma. Studies have found that individuals with asthma are more likely to have gum disease compared to those without asthma. While the exact relationship between the two conditions is not fully understood, it is believed that inflammation may play a role.
Both gum disease and asthma are characterized by chronic inflammation. Inflammation in the gums can release inflammatory markers into the bloodstream, which can affect the airways and exacerbate asthma symptoms. Additionally, the bacteria present in gum disease can trigger an immune response that may have an impact on respiratory health.
Taking care of your oral health is essential for maintaining overall respiratory health. Good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can help reduce the risk of gum disease and its potential impact on the respiratory system. It is also important for individuals with asthma to manage their condition effectively, following their doctor’s advice and taking any prescribed medications.
Gingivitis and Diabetes
Research has shown that there is a bidirectional relationship between gum disease and diabetes. Not only does diabetes increase the risk of developing gum disease, but gum disease can also make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels.
Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including gum infections. High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections, leading to a higher likelihood of developing gum disease. Additionally, gum disease can make it harder for individuals with diabetes to control their blood sugar levels, creating a vicious cycle.
The inflammation caused by gum disease can increase insulin resistance, making it more challenging for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels and further complications.
Controlling blood sugar levels and oral health
Maintaining good oral hygiene and controlling blood sugar levels are essential for individuals with diabetes to protect their overall health. Here are some tips for managing both:
- Brush and floss regularly: Proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Control blood sugar levels: Follow your doctor’s advice on managing diabetes, including taking medications as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can monitor the health of your gums and provide professional cleaning to remove any plaque buildup.
- Open communication: It’s important to inform both your dentist and healthcare team about your diabetes diagnosis and any changes in your blood sugar levels. This collaboration allows for a comprehensive approach to managing both diabetes and gum disease.
Gingivitis and Pregnancy
Research has shown that there is a connection between oral health, specifically gingivitis, and pregnancy complications. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of developing gingivitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the gums.

During pregnancy, hormonal shifts can lead to an exaggerated response to plaque, causing the gums to become more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This can result in symptoms such as redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of gum disease known as periodontitis, which has been associated with complications during pregnancy.
Studies have indicated that pregnant women with untreated gum disease may be at a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight babies. The bacteria from the infected gums can enter the bloodstream and potentially affect the developing fetus. Furthermore, the inflammation caused by gum disease may trigger an immune response that can contribute to pregnancy complications.
Preventive measures for expectant mothers
Taking care of oral health is crucial for expecting mothers in order to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications. Here are some preventive measures that pregnant women can take:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brushing teeth twice a day and flossing daily can help remove plaque and prevent the onset of gingivitis.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush: A soft-bristled toothbrush is gentler on the gums and can help prevent further irritation.
- Rinse with antimicrobial mouthwash: Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce the bacterial load in the mouth and promote gum health.
- Eat a balanced diet: A nutrient-rich diet can support overall oral health. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables and limit sugary snacks and beverages.
- Regular dental check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups throughout pregnancy to monitor oral health and address any concerns.
- Inform your dentist about your pregnancy: It is important to inform your dentist about your pregnancy and any changes in your medical history. This allows for appropriate adjustments in the dental treatment plan if needed.
By maintaining good oral hygiene practices and seeking regular dental care, expectant mothers can help protect their oral health and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications associated with gingivitis.
Gingivitis and Mental Health
Oral health plays a significant role in overall well-being, and studies have shown that poor oral health can have a negative impact on mental health. Issues such as gum disease, including gingivitis, can contribute to feelings of anxiety and low self-esteem, affecting a person’s mental well-being.
When individuals experience oral health problems like gingivitis, they may develop self-consciousness about their smile and worry about bad breath. These concerns can lead to social anxiety and a reluctance to engage in social activities, which can further impact mental health. The discomfort and pain associated with gum disease can also contribute to feelings of frustration and irritability, affecting an individual’s overall mood and mental state.
Anxiety, depression, and gum disease
Research has shown a bidirectional relationship between mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, and gum disease like gingivitis. On one hand, individuals experiencing anxiety or depression may neglect their oral hygiene, leading to the development of gum disease. On the other hand, the inflammation and chronic pain associated with gum disease can contribute to the development or worsening of mental health conditions.
Anxiety and depression can lead to a decrease in saliva production, affecting the mouth’s natural defense against bacteria. This can make individuals more susceptible to gum disease. Furthermore, the release of stress hormones associated with anxiety and depression can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum infections.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing mental health conditions to prioritize their oral health and seek appropriate dental care. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, along with regular dental check-ups, can help prevent and manage gum disease, reducing the negative impact on mental health.
Gingivitis and Autoimmune Diseases
Poor oral health, specifically periodontal disease, has been found to be associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune disorders. Studies have shown that individuals with periodontal disease are more likely to develop conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and psoriasis.
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. In periodontal disease, the immune system responds to the bacteria in the mouth, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. This chronic inflammation may trigger an immune response throughout the body, increasing the risk of developing autoimmune disorders.
Rheumatoid arthritis and its association with oral health
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Recent research has uncovered a strong association between rheumatoid arthritis and oral health, particularly periodontal disease.
It has been found that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to have severe periodontitis, a form of periodontal disease characterized by the loss of bone and connective tissue that supports the teeth. The chronic inflammation present in both conditions may be a contributing factor to their association.
Furthermore, the bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the systemic inflammation seen in rheumatoid arthritis. This bidirectional relationship between oral health and rheumatoid arthritis highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking appropriate dental care for individuals with autoimmune disorders.
Maintaining Oral Health to Prevent Gingivitis
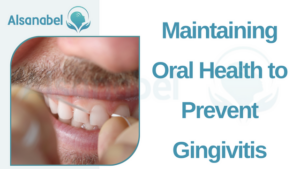
Proper brushing and flossing techniques
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial in preventing gingivitis and other dental problems. It is important to brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Pay particular attention to the gumline, where plaque tends to accumulate. Use gentle, circular motions to effectively remove plaque and bacteria.
Flossing is also essential for preventing gingivitis. Regular flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. It is recommended to floss at least once a day, preferably before bedtime. Be sure to use proper flossing technique, gently gliding the floss between each tooth and along the gumline, forming a C shape around each tooth to remove debris effectively.
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings
Regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining good oral health and preventing gingivitis. Dental professionals can detect early signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatment before it progresses. During a dental check-up, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums, perform a thorough cleaning, and provide guidance on proper oral hygiene practices.
Professional dental cleanings are necessary to remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be removed with regular brushing and flossing. The dental hygienist will use specialized instruments to remove the buildup and polish your teeth, leaving them clean and smooth.
By following proper brushing and flossing techniques and scheduling regular dental check-ups and cleanings, you can prevent gingivitis and maintain optimal oral health. Taking these preventive measures is especially important for individuals with autoimmune disorders, as poor oral health has been linked to an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases. Remember, a healthy smile starts with good oral hygiene habits.
Importance of addressing gingivitis for overall health
It is crucial to maintain proper oral hygiene to prevent gingivitis and other dental problems. By following the correct brushing and flossing techniques, individuals can effectively remove plaque and bacteria, particularly around the gumline. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for early detection and treatment of gum disease.
Addressing gingivitis is not just important for oral health but also for overall well-being. Research has shown a link between poor oral health and an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases. Therefore, individuals with autoimmune disorders should be especially vigilant in maintaining good oral hygiene habits.
Taking proactive steps for optimal oral hygiene
To prevent gingivitis and maintain optimal oral health, it is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be diligent in brushing all surfaces of your teeth and pay particular attention to the gumline.
Flossing is equally important for preventing gingivitis. Regular flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. Take the time to floss at least once a day, using a proper technique of gently gliding the floss between each tooth and forming a C shape around each tooth.
In addition to personal oral care, scheduling regular dental check-ups is crucial. Dental professionals can detect early signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatment before it progresses. Professional cleanings are also necessary to remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be eliminated through regular brushing and flossing.
