Introduction to Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation and bleeding of the gums. It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. The condition is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can irritate the gums, leading to it.
Causes of Gingivitis
The main cause of it is poor oral hygiene. When plaque is allowed to build up on the teeth, it can harden into tartar, which is much more difficult to remove. Tartar can irritate the gums and cause inflammation. Other factors that can contribute to the development of gingivitis include:
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anti-seizure drugs and some types of oral contraceptives, can increase the risk of it.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and reduces the ability of the gums to heal, making them more susceptible to infection.
- Systemic diseases: Conditions like diabetes and HIV/AIDS can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
- Genetic factors: Some people may be more genetically predisposed to developing it.
Dental Plaque and Gingivitis
Dental plaque plays a crucial role in the development of gingivitis. Plaque is a sticky film that forms on the teeth and contains harmful bacteria. When plaque is not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, also known as dental calculus. Tartar is much more difficult to remove and provides a perfect environment for bacteria to thrive.
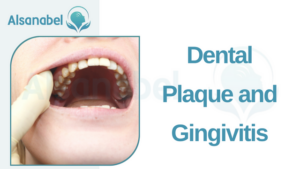
The bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding. This is the first stage of gum disease. The longer plaque and tartar remain on the teeth, the more severe the inflammation can become.
Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
It can manifest in several ways, and it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms to seek prompt treatment. Common signs of include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums
- Changes in the way teeth fit together when biting down
In addition to proper oral hygiene practices like brushing twice a day and flossing daily, regular dental check-ups are crucial to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Dentists can perform professional cleanings and provide guidance on maintaining good oral health. Taking preventive measures and addressing gingivitis in its early stages can help preserve gum and overall oral health. Remember, a healthy smile starts with healthy gums!
Poor Oral Hygiene and Gingivitis
Poor oral hygiene is a major contributing factor. When proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, are neglected, it allows dental plaque to accumulate on the teeth. This plaque contains harmful bacteria that can irritate and inflame the gums, leading to gingivitis.
Without regular brushing and flossing to remove plaque, it can harden into tartar or dental calculus. Tartar is even more difficult to remove and provides a hospitable environment for bacteria to thrive. As the bacteria in plaque and tartar multiply, they produce toxins that further irritate the gums and promote inflammation.
Preventive Measures for Gingivitis
Prevention is key when it comes to gingivitis. Taking proactive measures to maintain good oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing this gum disease. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Brushing twice a day: Using a soft-bristled toothbrush, gently brush your teeth for two minutes each time. Pay attention to all surfaces of your teeth, including the gumline.
- Flossing daily: Regular flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline, where a toothbrush may not reach.
- Using mouthwash: An antimicrobial mouth rinse can help reduce plaque and bacteria in the mouth. Look for a mouthwash that is specifically formulated for gum health.
- Maintaining a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while low in sugary and acidic foods, can promote good oral health.
- Avoiding tobacco products: Smoking and using other tobacco products can increase the risk of gum disease and hinder the healing process.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings is essential to removing plaque and tartar buildup. Dentists can also identify early signs of gingivitis and provide appropriate treatment.
Smoking and Gingivitis
Smoking is strongly associated with an increased risk of gingivitis. Research has shown that smokers are more likely to develop gum disease compared to non-smokers. The chemicals present in tobacco products can compromise the body’s immune response, making it harder for the gums to fight off infection and inflammation.
Effects of Smoking on Gum Health
- Reduced blood flow: Smoking constricts blood vessels, impeding proper circulation to the gums. This reduces the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen, making it difficult for the gums to heal and fight off infection.
- Delayed healing: Smokers may experience delayed healing of gum tissues. This means that the gums take longer to repair and recover from damage caused by gingivitis.
- Increased plaque buildup: Smoking promotes the accumulation of plaque on the teeth, as tobacco smoke can interfere with saliva production. Plaque buildup provides an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive, leading to further gum irritation and inflammation.
- Masked symptoms: Smoking can mask the symptoms of gingivitis, making it harder for individuals to recognize the early signs of gum disease. This delay in diagnosis and treatment can result in more severe gum problems down the line.
It is essential for smokers to be aware of the increased risk of gingivitis and take extra measures to maintain good oral hygiene. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to improve gum health and reduce the chances of developing gum disease. Additionally, regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are crucial for smokers to monitor their gum health and address any issues promptly.
Hormonal Changes and Gingivitis
Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy and puberty, can increase the risk of developing gingivitis. These changes in hormone levels can lead to increased blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to inflammation. Additionally, hormonal fluctuations can affect the body’s immune response, making it harder for the gums to fight off infection and inflammation.

During pregnancy, the rise in hormone levels can result in a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis. This condition typically occurs during the second and third trimesters and is characterized by swollen, red, and tender gums. If left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis.
Similarly, hormonal changes during puberty can also impact gum health. Puberty gingivitis is common among teenagers and is characterized by swollen, bleeding gums. Hormonal fluctuations during this time can increase the sensitivity of the gums and make them more susceptible to plaque buildup and bacterial infection.
Managing Gingivitis during Hormonal Changes
It is crucial for individuals experiencing hormonal changes to pay extra attention to their oral health. Here are some tips for managing gingivitis during hormonal changes:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria from the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacterial growth.
- Visit the dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring the health of your gums, particularly during hormonal changes. Your dentist can identify and treat gingivitis early before it progresses to more severe forms of gum disease.
- Eat a balanced diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can boost your immune system and promote gum health. Avoid sugary and acidic foods that can contribute to plaque buildup and gum inflammation.
- Practice stress management: Stress can worsen the symptoms of gingivitis. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercising, practicing relaxation techniques, or seeking support from friends and family.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and other tobacco products can worsen the symptoms of gingivitis and increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining good gum health.
Diabetes and Gingivitis
Research has shown a strong link between diabetes and gingivitis. People with diabetes are more prone to gum disease due to their compromised immune system and reduced ability to fight off infection. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can also contribute to gum inflammation and damage the blood vessels in the gums, making them more susceptible to infection.
Diabetic individuals may experience increased blood flow to the gums, causing them to become swollen, red, and tender. This condition, known as diabetic gingivitis, requires prompt attention and management to prevent it from progressing to more severe forms of gum disease.
Managing Gingivitis with Diabetes
- Maintain strict blood sugar control: Keep your blood sugar levels within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. This can help reduce the severity of gingivitis and prevent further complications.
- Practice thorough oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria from the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacterial growth.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. They can monitor the health of your gums and provide appropriate treatment or intervention if necessary.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients can promote gum health. Limit your intake of sugary and acidic foods, as they can contribute to plaque buildup and inflammation.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and using other tobacco products can worsen the symptoms of gingivitis and increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining good gum health.
By implementing these strategies, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage gingivitis and reduce the risk of complications. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare team, including your dentist, to develop a comprehensive oral care plan tailored to your specific needs. Early detection and treatment are crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
Medications and Gingivitis
Research has shown that certain medications can have an impact on gum health and increase the risk of gingivitis. Some examples of medications that can contribute to this include:
- Anticonvulsants: Drugs used to treat seizures, such as phenytoin, can cause gum overgrowth and inflammation, making the gums more susceptible to infection.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications prescribed to suppress the immune system, like cyclosporine, can weaken the body’s ability to fight off harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to an increased risk of gingivitis.
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications, commonly used to treat high blood pressure, can also cause gum overgrowth and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Oral contraceptives: Hormonal changes caused by birth control pills can affect gum health and make the gums more sensitive to plaque buildup.
Precautions for Gingivitis with Medications
If you are taking medications that may impact your gum health, it’s important to take extra precautions to prevent and manage gingivitis. Here are some steps you can take:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria from the gumline. Consider using an antibacterial mouthwash to further reduce bacterial growth.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. They can monitor the health of your gums and provide appropriate treatment or intervention if necessary.
- Communication with healthcare providers: Inform your dentist and healthcare provider about the medications you are taking. They can provide guidance on managing gum health and recommend any necessary adjustments to your oral care routine.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can worsen the symptoms of gingivitis and increase the risk of gum disease. If you are a smoker, quitting is essential for maintaining good gum health.
By being vigilant about your oral care routine and working closely with your healthcare team, you can mitigate the risks associated with medications and reduce the likelihood of developing or worsening gingivitis. It’s important to prioritize your gum health, as it plays a crucial role in your overall well-being.
Stress and Gingivitis
Research suggests that stress can have negative effects on gum health and contribute to the development and progression of gingivitis. When individuals are under high levels of stress, their immune system may become compromised, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums.

Additionally, stress can lead to behavioral changes that can worsen oral hygiene practices, such as increased snacking on unhealthy foods or neglecting regular brushing and flossing.
Stress Management for Gingivitis Prevention
To prevent or manage gingivitis caused by stress, it is important to incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Relaxation techniques: Practice activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being. These techniques can help calm the mind and body and reduce the impact of stress on gum health.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can not only improve overall health but also help reduce stress levels. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters and stress relievers. Incorporate activities you enjoy into your routine, such as jogging, swimming, or cycling.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit the consumption of sugary snacks and beverages, as they can contribute to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gingivitis. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and quit smoking, as these habits can worsen gum disease.
- Proper sleep hygiene: Ensure you get enough sleep each night, as lack of sleep can contribute to heightened stress levels. Develop a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and prioritize a restful sleep environment.
By effectively managing stress through these strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing or worsening gingivitis. Remember to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, as well as scheduling routine dental check-ups for professional cleanings and comprehensive evaluations of gum health.
Seeking Professional Help
It is important to seek professional help if you notice any symptoms of gingivitis or if you suspect that stress may be affecting your gum health. A dentist or periodontist can diagnose and treat gingivitis effectively. They may perform a thorough examination of your gums, take X-rays if necessary, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your specific needs. Professional interventions may include deep cleanings, scaling and root planing, and the use of antimicrobial agents to reduce inflammation and promote gum healing.
Preventing Gingivitis for Oral Health Maintenance
Prevention is key when it comes to maintaining oral health and preventing gingivitis. In addition to managing stress, there are several steps you can take to keep your gums healthy:
- Regular brushing and flossing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
- Regular dental check-ups: Schedule routine dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist. These visits allow for professional cleanings, early detection of gum problems, and necessary interventions to prevent gingivitis from progressing.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A balanced diet that is low in sugar and high in nutrients is essential for good oral health. Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Limit your intake of sugary snacks and beverages.
- Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and chewing tobacco can increase your risk of developing gum disease. Excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to gum problems. Quitting tobacco use and limiting alcohol intake can help protect your gums.
- Protect your oral health habits: Consistency in oral hygiene practices is crucial. Make sure you are using proper brushing and flossing techniques and replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
By following these preventive measures and seeking professional help if needed, you can maintain healthy gums and reduce the risk of gingivitis and other gum diseases. Remember, taking care of your oral health is an essential part of your overall well-being.
